
by Maureen Seel, RDN/LDN CDCES
If you have type 2 diabetes, chances are your doctor has recommended lifestyle changes to improve your blood glucose control. But what happens when diet and exercise aren’t enough? When diabetes medications are needed, health care providers generally have many...

by Maureen Seel, RDN/LDN CDCES
Type 1 diabetes completely damages the pancreas, an organ responsible for making insulin. For that reason, persons with type 1 diabetes cannot produce any insulin on their own. Every patient with type 1 diabetes depends on injections of insulin so that glucose can be...
by Maureen Seel, RDN/LDN CDCES
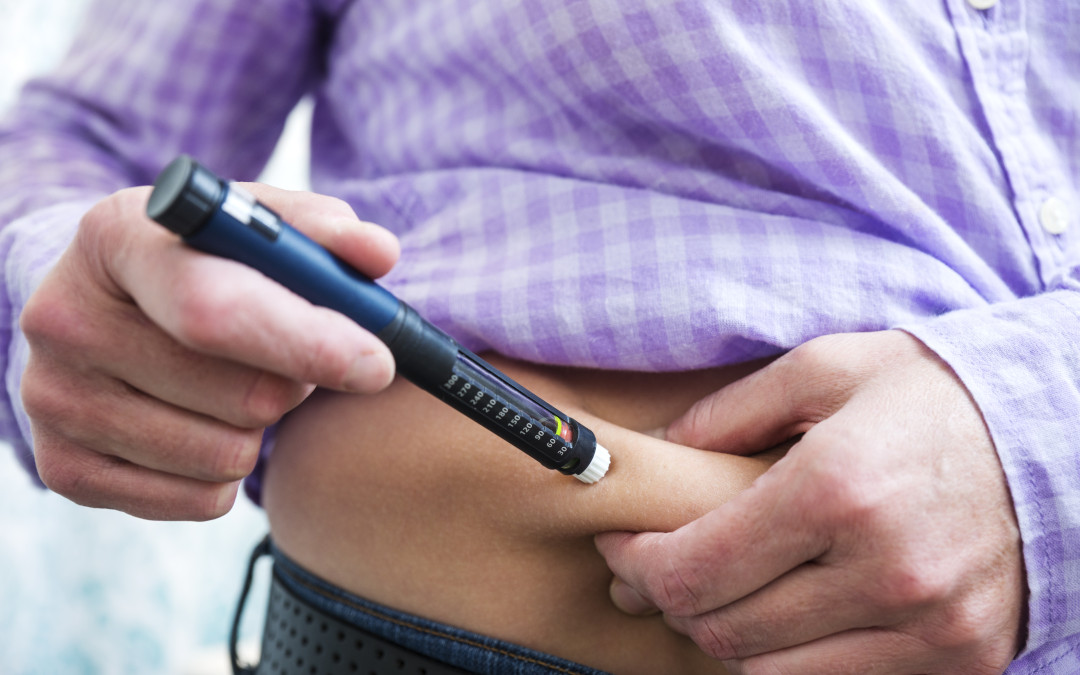
The decision to take insulin is never an easy one. For many patients, it comes after years of having type 2 diabetes and trying multiple weight-loss regimens, diets, and oral medications. For other patients, the decision to take insulin is made when blood glucose...
by Maureen Seel, RDN/LDN CDCES
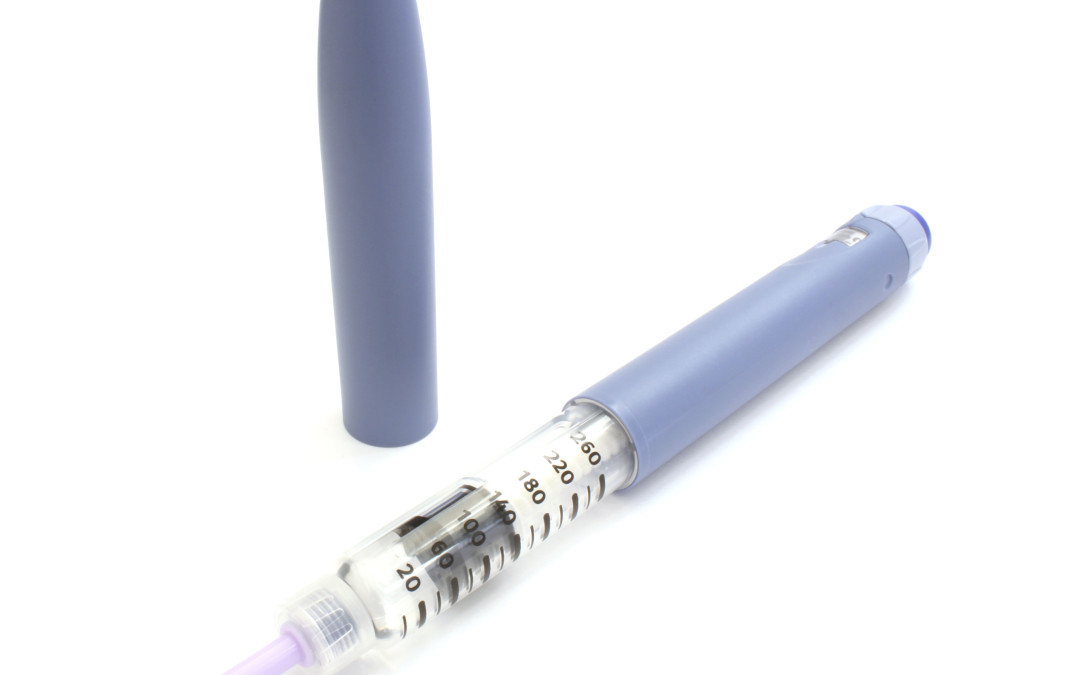
Who?Intermediate- and long-acting (basal) insulins are recommended for patients with type 1, type 2, or gestational diabetes. They may also be used in other types of diabetes (i.e. steroid-induced).Persons with type 1 diabetes generally use intermediate-acting insulin...

by Maureen Seel, RDN/LDN CDCES
Who? Short-acting (Regular) and rapid-acting insulins (Aspart, Lispro, Glulisine) are recommended for patients with type 1, type 2, or gestational diabetes. They may also be used in other types of diabetes. Persons with type 1 diabetes often use insulin regular or...





